QNN Backend Design¶
Overview¶
The QNN (Qualcomm Neural Network) Backend provides optimized execution of neural network models on Qualcomm’s AI Engine Direct (formerly SNPE/QNN SDK). This backend enables efficient deployment on Qualcomm-powered devices including smartphones, embedded systems, and edge AI platforms.
Key Features:
Hardware Acceleration: Leverages Qualcomm’s Hexagon DSP and HTP (Hexagon Tensor Processor)
Graph-Level Optimization: Executes entire subgraphs as optimized QNN graphs
Mixed Precision Support: INT8/INT16 quantization with dynamic scale propagation
Context Caching: Serializes compiled graphs to binary format for fast loading
Custom Operations: Extensible custom op support through QNN op packages
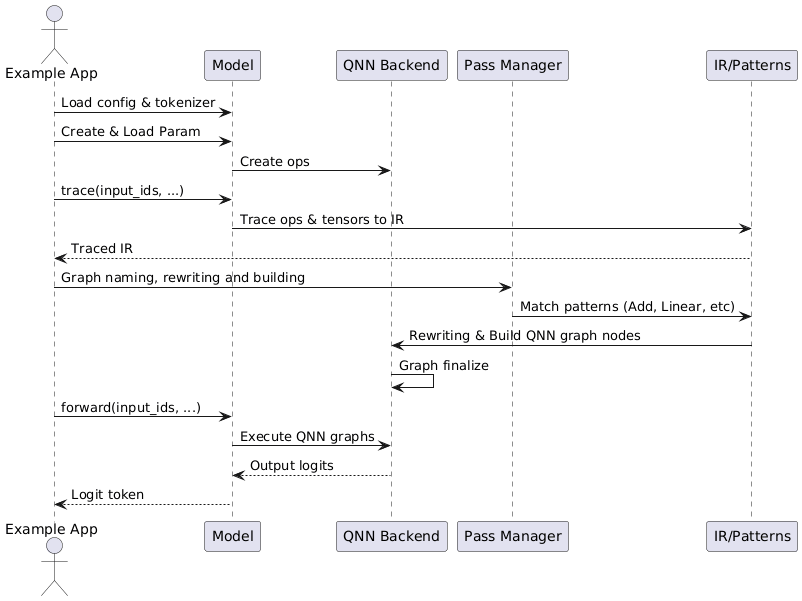
Figure 1: QNN Backend Execution Sequence.¶
Architecture Components¶
The QNN backend architecture consists of several key components working together:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ MLLM Framework │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ Module │ │ Layer │ │ Dispatcher │ │
│ └──────┬───────┘ └────-─┬───────┘ └──────┬───────┘ │
└─────────┼─────────────────┼─────────────────┼───────────────┘
│ │ │
└─────────────────┴─────────────────┘
│
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ QNN Backend Infrastructure │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ QNNBackend (Core Manager) │ │
│ │ - Runtime Management - Context Management │ │
│ │ - Graph Registry - Tensor Management │ │
│ └─────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌─────────┴──────────┬──────────────┬─────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ QNNRuntime QNNModel QNNDispatcher QNNGraphBuildPass
│ (SDK Interface) (Graph Mgmt) (Execution) (Compilation)│
│ │
└────────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────┘
│
┌────────────────────────────▼──────────────────────────────────┐
│ Qualcomm QNN SDK │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ QNN Interface│ │ QNN Context │ │ QNN Graph │ │
│ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Hardware Backends (HTP/DSP) │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
QNNBackend: Core Manager¶
The QNNBackend class serves as the central orchestrator for QNN operations:
Responsibilities:
Runtime Initialization: Manages QNN SDK initialization and device configuration
Context Management: Creates and maintains QNN execution contexts
Graph Registry: Maps graph names to
QNNModelinstancesTensor Management: Handles tensor creation, quantization, and data transfer
Performance Tuning: Configures power profiles and performance settings
Key Methods:
class QNNBackend : public Backend {
// Graph lifecycle management
std::shared_ptr<QNNModel> createQnnGraph(const std::string& graphName);
bool graphFinalize(const std::string& graphName);
void graphExecute(const std::string& graphName,
std::vector<Tensor>& inputs,
std::vector<Tensor>& outputs);
// Tensor management
bool addTensor(const std::string& graphName,
const std::string& tensorName,
Qnn_TensorType_t type,
const Tensor& tensor,
Qnn_QuantizeParams_t quantize);
// Component access
const QNN_INTERFACE_VER_TYPE& qnnInterface() const;
Qnn_BackendHandle_t backendHandle() const;
Qnn_ContextHandle_t context() const;
};
QNNRuntime: SDK Interface Layer¶
Manages low-level QNN SDK initialization and resource lifecycle:
Components:
Interface Loading: Dynamically loads QNN library symbols
Backend Selection: Initializes appropriate backend (HTP/DSP/GPU)
Device Management: Configures device-specific settings
Logging & Profiling: Optional debug and performance profiling
Initialization Flow:
// Create runtime with profiling
auto runtime = QNNRuntime::create(
ProfilingLevel::BASIC, // Enable profiling
QNN_LOG_LEVEL_WARN // Set log level
);
// Create execution context
Qnn_ContextHandle_t context;
runtime->createContext(context);
QNNModel: Graph Management¶
Represents a single QNN computational graph with complete lifecycle management:
Graph Lifecycle:
Initialization: Create graph with name and configuration
Tensor Addition: Register input/output/intermediate tensors
Node Addition: Add QNN operations with parameters
Finalization: Compile and optimize the graph
Execution: Run inference with input data
Key Operations:
class QNNModel {
// Initialization
ModelError_t initialize(const Qnn_ContextHandle_t& context,
const char* graphName,
bool debug);
// Tensor management
ModelError_t addTensor(const std::string& tensorName,
Qnn_TensorType_t type,
const Tensor& tensor,
Qnn_QuantizeParams_t quantize);
ModelError_t addStaticTensor(const std::string& tensorName,
const Tensor& tensor,
Qnn_QuantizeParams_t quantize);
std::shared_ptr<QNNTensorWrapper> getTensorWrapper(
const std::string& tensorName);
// Node management
ModelError_t addNode(Qnn_OpConfigVersion_t version,
const std::string& name,
const std::string& packageName,
const std::string& type,
const std::vector<...>& tensorParams,
const std::vector<...>& scalarParams,
const std::vector<std::string>& inputNames,
const std::vector<std::string>& outputNames);
// Finalization and execution
ModelError_t finalizeGraph(Qnn_ProfileHandle_t profileHandle,
Qnn_SignalHandle_t signalHandle);
bool isGraphFinalized() const;
};
Tensor Wrappers:
The backend uses C++ RAII wrappers to manage QNN’s C-style resources:
QNNTensorWrapper: Manages tensor metadata and data buffersQNNParamTensorWrapper: Wraps constant tensor parametersQNNParamScalarWrapper: Wraps scalar parameters
QNNDispatcher: Execution Engine¶
Handles task execution routing between CPU and QNN:
Execution Strategy:
void QNNDispatcher::process(const Task::ptr_t& task) {
switch (task->type) {
case TaskTypes::kExecuteOp: {
// Selective execution: only X2X and Embedding on QNN
task->op->reshape(task->inputs, task->outputs);
if (task->op->getOpType() == OpTypes::kX2X ||
task->op->getOpType() == OpTypes::kEmbedding) {
task->op->setup(task->inputs, task->outputs);
task->op->forward(task->inputs, task->outputs);
}
break;
}
case TaskTypes::kExecuteModule: {
// Full module execution on QNN
auto qnnBackend = getBackend(kQNN);
auto moduleName = getModuleName(task);
// Forward pass to populate outputs
task->outputs = module->forward(task->inputs, task->args);
// Execute the QNN graph
qnnBackend->graphExecute(moduleName,
task->inputs,
task->outputs);
break;
}
}
}
Execution Modes:
Op-Level: Individual operations (X2X, Embedding) executed separately
Module-Level: Entire subgraphs executed as optimized QNN graphs
QNNGraphBuildPass: Compilation Pipeline¶
Transforms MLLM IR into executable QNN graphs through pattern matching:
Compilation Flow:
IR Traversal: Iterate through
SubGraphOpnodes marked for QNNPattern Matching: Match MLLM operations to QNN operation patterns
Graph Construction: Build QNN graph with nodes and tensors
Optimization: Apply QNN SDK optimizations
Finalization: Compile graph for target hardware
Pattern Registration:
class QNNGraphBuildPass : public Pass {
QNNGraphBuildPass() {
// Register operation patterns
regPattern<QNNAddPattern,
QNNMulPattern,
QNNLinearPattern,
QNNRMSNormPattern,
QNNViewPattern,
QNNTransposePattern,
QNNX2XPattern,
QNNCastTypePattern,
QNNSiLUPattern>();
// Register custom ops
patterns_.emplace(
customOpId("DequantizeAdd"),
std::make_shared<QNNDequantizeAddPattern>()
);
}
};
Pattern Example:
class QNNLinearPattern : public QNNOpPattern {
bool addNode(const std::string& graphName,
const ir::linalg::LinalgIROp::ptr_t& op,
const std::vector<TensorValue::ptr_t>& inputs,
const std::vector<TensorValue::ptr_t>& outputs) override {
// Add input tensors
addTensor(graphName, inputs[0], QNN_TENSOR_TYPE_NATIVE);
addTensor(graphName, inputs[1], QNN_TENSOR_TYPE_STATIC);
// Add output tensor
addTensor(graphName, outputs[0], QNN_TENSOR_TYPE_NATIVE);
// Create QNN FullyConnected node
backend->graphAddNode(
graphName,
op->name(),
"FullyConnected",
{inputs[0]->name(), inputs[1]->name()},
{outputs[0]->name()},
{}, // tensor params
{} // scalar params
);
return true;
}
};
Execution Workflows¶
Compilation Workflow¶
The QNN backend compilation workflow transforms traced IR into executable graphs:
User Model (Python/C++)
│
├─── Model::trace() [trace_mode=true]
│ └─── Creates IR representation
│
▼
IR Module (mllm::ir::ModuleOp)
│
├─── Contains SubGraphOp(s) marked as DeviceTypes::kQNN
│
▼
QNNGraphBuildPass::run()
│
├─── For each QNN SubGraphOp:
│ │
│ ├─── backend->createQnnGraph(graphName)
│ │ └─── Creates QNNModel instance
│ │
│ ├─── Add graph input tensors
│ │ └─── qnnModel->addTensor(..., QNN_TENSOR_TYPE_APP_WRITE)
│ │
│ ├─── Traverse IR operations
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── Match to QNN patterns
│ │ │ └─── pattern->addNode(graphName, op, inputs, outputs)
│ │ │
│ │ └─── Create QNN ops with:
│ │ ├─── Tensor parameters (weights, constants)
│ │ ├─── Scalar parameters (hyperparameters)
│ │ ├─── Input tensor names
│ │ └─── Output tensor names
│ │
│ └─── backend->graphFinalize(graphName)
│ │
│ ├─── qnnModel->finalizeGraph(...)
│ │ └─── Calls qnnInterface.graphFinalize()
│ │ └─── QNN SDK optimizes and compiles graph
│ │
│ └─── Graph ready for execution
│
▼
Compiled QNN Graphs (ready for inference)
Code Example:
// In QNNGraphBuildPass::buildQnnGraph()
void QNNGraphBuildPass::buildQnnGraph(
const ir::graph::SubGraphOp::ptr_t& sub_graph_op) {
auto qnn_backend = getQNNBackend();
std::string graph_name = sub_graph_op->getSymbolAttr()->str();
// Create QNN model
auto qnn_model = qnn_backend->createQnnGraph(graph_name);
// Add graph inputs
for (auto& input : sub_graph_op->inputs()) {
auto input_tensor = input->cast_<TensorValue>();
auto quantize_param = createQuantizeParams(input_tensor->tensor_);
qnn_model->addTensor(input_tensor->name(),
QNN_TENSOR_TYPE_APP_WRITE,
input_tensor->tensor_,
quantize_param);
}
// Process operations
for (auto& region_op : graph_region->ops()) {
if (auto linalg_op = cast<LinalgIROp>(region_op)) {
auto op_types = linalg_op->getAOpTypes();
if (patterns_.contains(op_types)) {
patterns_[op_types]->addNode(
graph_name, linalg_op,
op_inputs, op_outputs
);
}
}
}
// Finalize graph
qnn_backend->graphFinalize(graph_name);
}
Runtime Execution Workflow¶
Standard inference execution through the dispatcher system:
Application::forward()
│
├─── Module::forward() [DeviceTypes::kQNN]
│ │
│ ├─── Module::__main()
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── Task::createExecuteModuleTask()
│ │ │ └─── task->custom_context_ptr = module
│ │ │
│ │ └─── DispatcherManager::submit(qnn_dispatcher_id, task)
│ │
│ ▼
QNNDispatcher::receive(task)
│ │
│ └─── QNNDispatcher::process(task)
│ │
│ ├─── case kExecuteModule:
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── Extract module name
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── Call module->forward() to setup outputs
│ │ │ └─── Creates output tensor shapes
│ │ │
│ │ └─── qnnBackend->graphExecute(moduleName, inputs, outputs)
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── Lookup QNNModel by name
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── Copy input data to QNN tensors
│ │ │ └─── Handles quantization if needed
│ │ │
│ │ ├─── qnnInterface.graphExecute()
│ │ │ └─── QNN SDK executes on HTP/DSP
│ │ │
│ │ └─── Copy output data from QNN tensors
│ │ └─── Handles dequantization if needed
│ │
│ └─── case kExecuteOp:
│ └─── Execute X2X/Embedding ops individually
│
▼
Output Tensors (returned to application)
Quantization Support¶
The QNN backend provides comprehensive quantization support for efficient inference:
Quantization Metadata Management¶
Quantization scales are attached to tensors as metadata:
// Set quantization scale
inline void setQuantScale(Tensor& tensor, float scale) {
auto scale_view = std::make_shared<TensorView>(
Tensor::empty({1}, kFloat32, kCPU).alloc()
);
scale_view->ptr<float>()[0] = scale;
tensor.attachedViews()[QNN_QUANT_SCALE_NAME] = scale_view;
}
// Get quantization scale
inline float getQuantScale(Tensor& tensor) {
if (!tensor.attachedViews().contains(QNN_QUANT_SCALE_NAME)) {
return 1.0f; // Default scale
}
return tensor.attachedViews()[QNN_QUANT_SCALE_NAME]->ptr<float>()[0];
}
QNN Quantization Parameters¶
Convert MLLM quantization to QNN format:
Qnn_QuantizeParams_t createQuantizeParams(const Tensor& tensor) {
if (tensor.dtype() == kInt8 || tensor.dtype() == kInt16) {
float scale = getQuantScale(tensor);
return Qnn_QuantizeParams_t{
QNN_DEFINITION_DEFINED,
QNN_QUANTIZATION_ENCODING_SCALE_OFFSET,
{.scaleOffsetEncoding = {
.scale = scale,
.offset = 0 // Zero-point offset
}}
};
}
// Undefined quantization for float tensors
return DEFAULT_QUANTIZE_PARAMS;
}
Scale Propagation¶
Quantization scales propagate through reshape operations:
void propagateQuantScale(const Tensor& input, Tensor& output) {
if (input.dtype() == kInt8 || input.dtype() == kInt16) {
float scale = getQuantScale(input);
setQuantScale(output, scale);
}
}
Custom Operations¶
The QNN backend supports custom operations through the QNN Op Package mechanism:
DequantizeAdd Custom Op¶
A custom fused operation combining dequantization and addition:
Purpose:
Fuse int8 dequantization with element-wise addition
Improve accuracy for quantized models
Usage Example:
// In QwenAttentionProjNPU
class QwenAttentionProjNPU : public nn::Module {
nn::qnn::DequantizeAdd q_proj_dequantize_add_;
nn::qnn::DequantizeAdd k_proj_dequantize_add_;
nn::qnn::DequantizeAdd v_proj_dequantize_add_;
QwenAttentionProjNPU(const std::string& name, const QwenNPUConfig& cfg)
: nn::Module(name) {
// Register custom ops
q_proj_dequantize_add_ = reg<nn::qnn::DequantizeAdd>(
"self_attn.q_proj_dequantize_add"
);
// ...
}
};
Pattern Registration:
// In QNNGraphBuildPass constructor
patterns_.emplace(
Context::instance().lookupCustomizedOpId(kQNN, "DequantizeAdd"),
std::make_shared<QNNDequantizeAddPattern>()
);
Performance Optimization¶
Power Configuration¶
The QNN backend provides power profile management:
class QNNPerf {
void setPowerConfigBurst() {
// High performance mode
// - Maximum clock frequencies
// - Higher power consumption
// - Lower latency
}
void setPowerConfigBalanced() {
// Balanced mode
// - Moderate clock frequencies
// - Balanced power/performance
// - Medium latency
}
void setRpcLatencyAndPolling() {
// Configure RPC latency for HTP communication
}
};
Profiling Support(TODO)¶
Note
This is not yet implemented. Better profiling info printing should be added.
Enable detailed profiling for performance analysis:
enum class ProfilingLevel {
OFF, // No profiling
BASIC, // Basic timing information
DETAILED, // Detailed layer-wise profiling
INVALID
};
// Create runtime with profiling
auto runtime = QNNRuntime::create(
ProfilingLevel::DETAILED,
QNN_LOG_LEVEL_INFO
);
Context Serialization¶
Note
TODO: Context retrieve should support retrieve by file name and dynamic switching.
Serialize compiled graphs to avoid recompilation:
// Save context to binary file
qnn_backend->saveContext("qnn_context.bin");
// Load pre-compiled context
Qnn_ContextHandle_t context;
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<QNNModel>> models;
runtime->retrieveContext(context, models);
Best Practices¶
Graph Partitioning¶
For optimal performance, partition your model strategically:
Guidelines:
QNN Subgraphs: Place compute-intensive operations (Linear, Conv, Attention)
CPU Operations: Keep dynamic operations (KVCache, RoPE) on CPU
Minimize Data Transfer: Reduce tensor copies between QNN and CPU
Example Partitioning:
class QwenDecoder : public Module {
// QNN: Attention projections
QwenAttentionProjNPU self_attn_proj_; // -> kQNN
// CPU: KV cache and RoPE
QwenAttentionMatmul self_attn_matmul_; // -> kCPU
// QNN: Output projection and MLP
QwenOutProjAndMLP self_attn_out_mlp_; // -> kQNN
};
Quantization Strategy¶
Recommendations:
Per-Tensor Quantization: Attach scales to input/output tensors
Scale Initialization: Set scales during model loading
Dynamic Range: Use calibration data to determine optimal scales
Precision: INT8 for most operations, INT16 for critical layers
// During model loading
void loadQuantizedModel(const ParameterFile::ptr_t& params) {
for (auto& [name, tensor] : *params) {
if (tensor.dtype() == kInt8) {
// Scale stored in parameter file
float scale = params->getScale(name);
setQuantScale(tensor, scale);
}
}
}
Error Handling¶
Always check return codes from QNN operations:
#define CALL_QNN(apiCall) do { \
int errorCode = ((apiCall) & 0xFFFF); \
if (errorCode != QNN_SUCCESS) { \
MLLM_ERROR("QNN Error in {}, line {}: error code {}", \
__FILE__, __LINE__, errorCode); \
assert(errorCode == QNN_SUCCESS); \
} \
} while (0)
// Usage
CALL_QNN(qnnInterface.graphFinalize(graph, nullptr, nullptr));
Troubleshooting¶
Common Issues¶
Issue: Graph finalization fails
Cause: Incompatible tensor dimensions or unsupported operations
Solution: Check QNN SDK documentation for supported ops and constraints
Issue: Incorrect output values
Cause: Quantization scale mismatch or missing scale propagation
Solution: Verify quantization scales are correctly set and propagated
Issue: Performance degradation
Cause: Excessive CPU-QNN data transfers or suboptimal partitioning
Solution: Profile with Perfetto, optimize graph boundaries
Debug Logging¶
Enable verbose QNN logging:
auto runtime = QNNRuntime::create(
ProfilingLevel::DETAILED,
QNN_LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE // Maximum verbosity
);
API Reference¶
QNNBackend API¶
class QNNBackend : public Backend {
public:
// Graph lifecycle
std::shared_ptr<QNNModel> createQnnGraph(const std::string& graphName);
bool graphFinalize(const std::string& graphName);
void graphExecute(const std::string& graphName,
std::vector<Tensor>& inputs,
std::vector<Tensor>& outputs);
// Tensor management
bool addTensor(const std::string& graphName,
const std::string& tensorName,
Qnn_TensorType_t type,
const Tensor& tensor,
Qnn_QuantizeParams_t quantize = DEFAULT_QUANTIZE_PARAMS);
bool addStaticTensor(const std::string& graphName,
const std::string& tensorName,
const Tensor& tensor,
Qnn_QuantizeParams_t quantize = DEFAULT_QUANTIZE_PARAMS);
std::shared_ptr<QNNTensorWrapper> getTensorWrapper(
const std::string& graphName,
const std::string& tensorName);
// Node management
void graphAddNode(const std::string& graphName,
const std::string& nodeName,
const std::string& nodeType,
const std::vector<std::string>& inputTensorNames,
const std::vector<std::string>& outputTensorNames,
const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<QNNParamTensorWrapper>>& tensorParams,
const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<QNNParamScalarWrapper>>& scalarParams,
const std::string& packageName = "qti.aisw");
// Properties
bool isWeightOnDevice() override;
const QNN_INTERFACE_VER_TYPE& qnnInterface() const;
Qnn_BackendHandle_t backendHandle() const;
Qnn_ContextHandle_t context() const;
};
For more information on the overall framework architecture, see MLLM Framework Core Architecture.